The Miracle of the Human Genome
by Ronald P. Millett
Reprinted from Meridian Magazine (Sept. 25, 2000)
The human genome contains the programmed codes of life which may be surprisingly similar to modern computer programs. Now that the recording of the entire code is nearly complete, software engineers turned biologists may begin to understand those complicated programs.
 |
Model of a tiny part of a DNA Molecule
The recent history making research to sequence the code of the entire human DNA(1) "genome" shows us as never before the complexity and hierarchy of systems necessary for the miracle of life. As scientists unravel this DNA "book of life," researchers are finding that living systems have many parallels with information processing systems. Just as Alma testified that "all things denote there is a God" (Alma 30:44), these discoveries testify of the hand of God in the creation of man and life on earth.
As Moroni began to write on the golden plates after the death of his father, Mormon, he delivered an impassioned plea for us to believe in the miracles of the Lord:
Behold, are not the things that God hath wrought marvelous in our eyes? Yea, and who can comprehend the marvelous works of God? Who shall say that it was not a miracle that by his word the heaven and the earth should be; and by the power of his word man was created of the dust of the earth; (Mormon 9:16-17)
King Benjamin affirmed the miracle of the Lord's creation and our obligation to be humble about our current understanding of his work.
Believe in God; believe that he is, and that he created all things, both in heaven and in earth; believe that he has all wisdom, and all power, both in heaven and in earth; believe that man doth not comprehend all the things which the Lord can comprehend. (Mosiah 4:9)
Our modern prophet Gordon B. Hinckley also added his testimony of the creation of man's miraculous body. "I believe the human body to be the creation of divinity. Our bodies were designed and created by the Almighty to be the tabernacles, the earthly receptacles, of our eternal spirits."(2)
Although there are disagreements among religious scientists about the mechanisms and specific natural laws that the Lord may have used in his creative processes, they recognize his hand in the miraculous diversity and complexity of life on earth and in the marvelous inventions that have been revealed to help us understand his works.(3)
Sequencing the Human Genome
One of the most ambitious scientific projects during this last decade has been the application of new technologies to determine the sequences of human DNA. The entire set of all DNA sequences is called the "genome." As the first pass through this project now is near completion, it is being described as a "day for the ages" similar to Galileo's discoveries, Lewis and Clark's exploration of the western United States and putting a man on the moon. One scientist said that for the first time we can now read "our own instruction book. Today, we celebrate the revelation of the first draft of the human book of life."Another scientist ventured that "the human genome project will be seen as the outstanding achievement, not only of our lifetime, but perhaps in the history of mankind."(4)
Adding a note of caution to the announcement, James Watson, co-discoverer of DNA in 1953, indicated decades of work are ahead of us before we actually understand how the products of all the genes in the genome interact with one another. "People say we can read it. We can't read it. We have the book, and now we've got to learn how to read it."(5) Geneticist Norton Zinder compared what we have yet to learn about the human genome to the history of the medical profession when the first book on human anatomy was published in 1543: "Even though that book identified almost all the parts of the human body, physicians today still struggle to understand how many of them work and interact. A similarly daunting task one that scientists say may also take several centuries to complete now awaits those who seek to make sense of the myriad genes of the human genome."(6)
Understanding the DNA "Book of Life"
 |
The genome "book" is a 3-billion-long
sequence of only four different "letters"
arranged in the DNA double helix.
This "book of life" is written as a sequence of only four different "genetic letters": the nucleotides thymine (T), cytosine (C), adenine (A) and guanine (G). The sequence is over three billion letters long, and it is the transcribing of that sequence which is now being completed. The series of these four nucleotides is coiled along the extremely long DNA spiral. This code is contained in each of the trillions of cells of the human body. If unraveled from a single cell, it would be over six feet long, but only 50 trillionths of an inch wide. For the areas of the DNA that define proteins, groups of only three of the genetic letters form a "genetic word" that specifies one of the 20 amino acids. The three billion genetic letters of the human genome contain about the same amount of information that can be stored on a typical CD-ROM.
The fact that every cell contains the entire human genome is amazing. It is as if every nut and bolt of a Boeing 747 contained the blueprint for constructing every part of the entire airplane, as well as assembly instructions.
It is estimated that only about 3% of the genetic code contains the protein defining sequences of the estimated 30,000 to 120,000 genes for human beings. The full genes themselves including these protein definitions and other less understood functions are estimated to be less than 10% of the total DNA. Much of the remaining 90% of the DNA code is known as "noncoding DNA" and most of its function is still poorly understood. Large portions of this noncoding DNA consists of sequences that appear to have no function at all and are referred to as "junk DNA."(7)
The differences between individual human beings is limited to one genetic letter in every thousand or only about three million genetic letters.(8) These differences could be easily stored on a floppy disk. This is an incredibly small amount of information to describe the combined differences among all the people of the world. This small amount of DNA difference among people has to be able to specify attributes as varied as individual eye color, facial characteristics, and differences in brain neuron connections. A single wrong or missing DNA letter or word in a gene's DNA formula can often be the culprit behind such genetic diseases as sickle cell anemia and cystic fibrosis.(9) The different versions of genes are called alleles. The gene that controls ear lobe shape has two alleles, one for attached ear lobes and one for free ear lobes. Since the total number of genes with variations is estimated to be one third of all genes, the average difference between alleles would be only about 20 to 60 bytes of information.(10) The information content of these DNA differences between humans is very high from a computer science perspective.
Levels of Systems to Process Information
DNA apparently contains high level genetic information letters and words that have tremendous influence on both the cellular and organism levels of life. That is, whether one's ear lobes are attached or free could be determined by a single letter of the entire genome, but that letter would in turn control extremely complicated processes that contain instructions on exactly how to produce that type of ear lobe. If so, then computer information theory may provide a useful framework to analyze how these levels of processing might work.
In computer science, a highly compressed data representation requires more complex programming layers to process than does uncompressed data. For example, an image of a 11 x 14 inch color painting took 53 million bytes in its uncompressed ("TIFF") file format. The same full page version took only about 1/100th as many bytes using a compressed ("JPEG") file format. The programming necessary to process the uncompressed representation is fairly simple, consisting of a few lines of programming code. However, the programming sequences to process the compressed version is much more complex, involving hundreds of lines of instructions and multiple nested programs.(11)
If we were to display this compressed photograph on a PC, other layers of programming would also be required. These would include the PC operating system such as Microsoft Windows® which consists of programs necessary to schedule and run programs and interface with other devices such as the video display.
These programming layers contain bits of information especially coded to reference the instructions of the computer hardware that it is designed to run on. Without the hardware, the software designs and programs cannot function and are only an intellectual exercise. In this example, the software is programmed to use instructions of the Intel Pentium® chip.
At the most basic level, the computer hardware works because of electrical power and the consistent operation of the laws of physics. Without electricity, the computer chips are just fancy sand etchings and the software programs are simply magnetic or optical patterns on a plastic or metal disk.
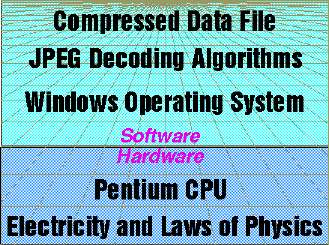 |
Figure 1. Levels of programming
required to display a photo.
Figure 1 illustrates this sample hierarchy of systems required to display on a PC a "JPEG" graphics file located on a remote server on the web.
Bioinformatics A New Field in Biology
With the new discoveries of how DNA contains coded information and being able to determine its actual genetic letter sequences, biology is becoming a field where information science plays an increasingly important role. A new kind of biologist is becoming part of the research teams that work to understand the meaning of the DNA code. This new field of "bioinformatics ... also called biological computing, straddles the lines dividing biology, computer science and mathematics."(12) Many of the key processes necessary to understand the DNA code are similar to the "reverse engineering" process that software developers go through to understand the functions of a program where no source code is available.(13)
As the sequences of the entire DNA molecule are being further studied, we are beginning to understand the large portions of the human genome that do not contain protein encoding sequences. Sequences called "Introns" are found between the "exon" protein encoding sequences of genes. Although we still know very little about what they might do, some scientists believe that introns may contain error detection and correction codes.(14) DNA mutations come from many sources: biological, chemical or radiation. The cell's DNA repair systems are able to correct most of these DNA changes. That would imply some very sophisticated error correction schemes. An example of a programming system that required complex error detection and corrections codes is the NASA Galileo deep space probe that is still orbiting the planet Jupiter. Extensive data compression and sophisticated error correction schemes have salvaged the Galileo mission even when the main antenna failed and the only the small backup antenna with one ten thousandth its capacity was left.(15)
Finding and understanding DNA sequences that control the actual regulation and activation of genes is barely in its infancy. However, in recent research comparing mouse DNA sequences to those of human DNA, "a research team from several universities found a regulatory region that governs three genes for proteins that influence the immune response."(16) This and other discoveries point to the existence of programming and control sequences that also reside in the DNA molecule.(17)
Parallel Information Systems
We are finding more and more evidence that DNA contains both genes that define actual proteins and sequences that control the relationships and activation of those genes. This relationship is similar to that of data ("objects") and their associated logic ("methods") in computer programming. We might also expect that parallels may be found to exist in biological systems to other layers in our layers of systems necessary to make a computer program work.
If a computer program needs an operating system to run, what might a DNA program need to be able to run? There are many chemical processes in a cell that are essential to "execute" the DNA programs. These include the various kinds of RNA molecules that copy and move DNA gene codes around the cell to be used in constructing proteins.(18) A recent article studying ribosomes where proteins are manufactured adds evidence of the complexity of "tunnel structures" where proteins are assembled.(19) These discoveries are reminiscent of the complex "pipeline"architectures of computer chips and data caching software.
Spiritual DNA?
When the Lord returns to earth for his Millennial reign, the scriptures tell us that he will reveal many truths about the creation. They will be especially exciting to those scientists who have been struggling to understand how he created and organized life on earth.
Yea, verily I say unto you, in that day when the Lord shall come, he shall reveal all things Things which have passed, and hidden things which no man knew, things of the earth, by which it was made, and the purpose and the end thereof (D. & C. 101:32-33)
One of the most exciting things that we hope to learn about would be the relationship of physical DNA to the "spiritual DNA"(13) or other forms of spirit matter that exists as part of the earlier spiritual creation of life on earth. The Lord has said that "I, the Lord God, created all things, of which I have spoken, spiritually, before they were naturally upon the face of the earth." (Moses 3:5). President Joseph F. Smith taught that "Man is a dual being, composed of the spirit which gives life, force, intelligence and capacity to man, and the body which is the tenement of the spirit ... and acts in harmony with it .... The two combined constitute the soul."(20)
In its December 1999 issue, Scientific American magazine contained an article entitled "How the Brain Creates the Mind" that predicted that in the coming fifty years we would unravel the mystery of how the conscious mind is derived only from the physical cells of the brain without any reference to the spirit portion of the human soul. Considering the mechanisms of how the spirit affects both the development of the brain as well as its function, one reviewer suggested that a future article might be better titled "How the Mind Creates the Brain."(21)
In a hierarchy of computer systems, the software layers require hardware layers to function. Similarly, we understand that the physical body would be lifeless without the spirit. The various systems that comprise the body would not function without the corresponding underlying spiritual systems.
Spiritual "Electric" Force
In Section 88 the Lord describes a life force called the "Light of Christ" which "proceedeth forth from the presence of God to fill the immensity of space The light which is in all things, which giveth life to all things ...." (D. & C. 88:12-13). President Joseph F. Smith explained that "it is the light of Christ, the Spirit of Truth, which proceeds from the source of intelligence, which permeates all nature, which lighteth every man and fills the immensity of space. You may call it the Spirit of God, you may call it the influence of God's intelligence, you may call it the substance of his power, no matter what it is called, it is the spirit of intelligence that permeates the universe and gives to the spirits of men understanding."(22)
Surely this light of Christ is another essential systems layer that enables the life processes specified in the miraculous human DNA molecule. Without its sustaining power, all life would wither away and die.(23)
 |
Figure 2. Life system parallels
to programming system.
Figure 2 illustrates a proposed life system architecture that has parallels with the programming system layers discussed earlier. Some of these layers will be able to be further investigated by scientific inquiry. The spiritual layers will doubtless be topics of study when the Lord comes again to reveal all things.
God's Majesty and Power
This is an exciting age to live in. As the Lord continues to pour out knowledge from heaven upon latter-day saints and the modern world we react with awe and wonder as we see his creations revealed. Dr. Francis Collins, the director of the human genome project said: "When something new is revealed about the human genome, I experience a feeling of awe at the realization that humanity now knows something only God knew before."(24)
Gregor Mendel, an Augustinian monk who was the founder of modern genetics, exemplified an objective scientist with a powerful faith in God. As well as his superb scientific writings, Mendel is the author of religious writings such as this poem:
Wherefore was man created? . . .
Assuredly the Most High, who so wisely
Shaped the round world . . .
Created man also
For some definite reason. Assuredly
The capacities of the mind
Prove that for it a lofty aim
Is reserved(25)
As we continue to learn more about DNA and are able to extract and recombine DNA sequences into living cells, surely we will better understand that we are the spiritual children of God. We are learning about his works of creation and being allowed to actually do a portion of that creative work. When Jesus was condemned for claiming to be the Son of God, "Jesus answered them, Is it not written in your law, I said, Ye are gods? ... If I do not the works of my Father, believe me not. But if I do ... believe the works" (John 10:34, 37-38, Psalms 82:6)
Our view of his creations varies all the way from the large and far away quasars of astronomy using telescopes to the intricate programming of the DNA molecule using microscopic techniques. The Lord's explanation in Section 88 that all these creations show his "majesty and power" surely applies to this tiny world of molecules as well as the giant worlds of planets and stars.
Behold, all these are kingdoms, and any man who hath seen any or the least of these hath seen God moving in his majesty and power. (D&C 88:43, 47)
Whether discovered by science or revealed by the Lord, the truth will not contradict itself. True science and true revelation will be a combined testimony of the marvelous work that the Lord has wrought and is bringing to pass here on earth. It will be a testimony also of his most important work and "glory to bring to pass the immortality and eternal life of man" (Moses 1:39).
About the Author
Ron Millett and his wife Rhonda live in Orem, Utah with their six energetic children. Ron is a software developer with a master's degree from BYU in computer science and the inventor of five software patents. He enjoys scouting, amateur astronomy with an observatory on his roof, and studying snakes. Rhonda enjoys being at home and is the webmaster of the ethington.org family history site.
Notes
- Deoxyribonucleic acid.
- Gordon B. Hinckley, Standing for Something, Random House, New York, 2000, p. 92.
- Elder Bruce R. McConkie explained that"as a result of this outpouring of the Lord's power the great inventions and advancements of modern times have been made possible." Bruce R. McConkie, Mormon Doctrine, Bookcraft, Salt Lake City, 1966, p. 753.
- Paul Recer, "Scientists Announce DNA Mapping," AP Science Writer, June 26, 2000, www.washingtonpost.com/wp-srv/aponline/20000626/aponline104637_000.htm.
- Rick Weiss and Justin Gillis, "Teams Finish Mapping Human DNA," Washington Post,June 27, 200, page A01. See Also: Michael Lemonick, "The Genome is Mapped: Now What?" Time Magazine, Vol. 156 No. 1, New York: July 3, 2000, p. 24. Even after loose ends of the sequencing process are cleared up "the so-called book of life will remain unreadable. That's because... 'It's written in a foreign language. It is a very complicated problem. It's going to be a long time coming.'" (Gerald Rubin, VP for research at Hughes Medical Institute )
- J. Travis, "Human Genome Work Reaches Milestone," Science News, Science Service,Washington, D. C.: July 1, 2000, Vol 158, No 1, p. 5.
- "DOE Human Genome Program," Primer on Molecular Genetics, U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Energy Research, 1992, www.ornl.gov/hgmis/publicat/primer/primer.pdf, p. 6-7.
Lemonick, op. cit., p. 27. "Scientists look for genes, which make up only about 3% of the genome."
"Pseudogenes, retropseudogenes, satellites, minisatellites, microsatellites, transposons and retrotransposons are all collectively known as 'junk DNA,' or sometimes, probably more accurately, as 'selfish DNA.' ...
"The commonest of retrotransposons is a sequence of 'letters' known as a LINE-1. This is a 'paragraph' of DNA, between a thousand and six thousand 'letters' long, that includes a complete recipe for reverse transcriptase near the middle. ... They account for a staggering 14.6% of the entire genome, that is, they are nearly five times as common as 'proper' genes. ...
"Even commoner than LINE-1 are shorter 'paragraphs' called 'Alus' [80 to 280 letters in length]. ... The Alu text may be repeated a million times in the human genome amounting to perhaps ten per cent of the entire 'book.' ...
"Pseudogenes are ... rusting wrecks of genes. ... for every working gene, there are a handful of wrecked copies elsewhere in the genome."
Matt Ridley, "Pseudogenes," www.math.auckland.ac.nz/~king/Preprints/book/upd/millupd/line.htm.
This description of pseudogenes reminds the author of programs where various older versions of a particular function are still linked into the executable image but not referenced in the main flow of programming logic.
- "DOE Human Genome Program," op. cit., p. 27.
- Alan Wildeman, "Molecular Biology and Genetics," University of Guelph, Ontario, Canada, www.uoguelph.ca/mbgwww/courses/40202/F99.html
"The gene responsible for CF, the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR).... The most common mutation, found in 90% of CF patients (70% of CF alleles), is loss of a single amino-acid (phenylalanine 508, DF508) within the CFTR protein. The mutant DF508 protein is incorrectly processed by the secretory pathway of the cell and fails to reach the plasma membrane."
W. H. Colledge, "Cystic Fibrosis," 1998, www.physiol.cam.ac.uk/staff/colledge/cysticfibrosis.htm
"What is sickle cell disease? The term sickle cell disease refers to a group of genetic disorders characterized by the presence of sickle hemoglobin (HbS), anemia, and acute and chronic tissue injury secondary to blockage of blood flow by abnormally shaped red cells. Normal hemoglobin, hemoglobin A (Hb A), is composed of two alpha ( [alpha] ) globin chains and two beta ( [beta]) globin chains. In Hb S, the [alpha] chain is the same as in Hb A, but the [beta] globin chain differs from the normal by the substitution of valine for glutamic acid at the sixth position ( [beta][sup s])."
National Institute of Health, "Sickle Cell Disease: Screening, Diagnosis, Management, and Counseling in Newborns and Infants, Clinical Guideline Number 6" text.nlm.nih.gov/ahcpr/sickle/www/scdctxt.html.
- With one third of genes having different alleles, assume 120,000 / 3 = 40,000 genes with different alleles. Using the figure of 750,000 bytes of variation among humans divided by the number of genes with alleles gives about 19 bytes average allowed difference between a pair of alleles. If there are only 30,000 genes the number would be 57 bytes difference. This would also assume that all of the 750K of variations among human beings occurs in the 3% gene area of the genome. If junk DNA also has variations, which at least some of it does for genetic fingerprinting, the average allowed difference per gene allele would be even less. The reference for the fraction one third is the following.
"The position occupied by a gene on a chromosome is its locus (plural loci), which is like its address. Although it is usual to talk about gene mapping, in many cases it is the loci of the genes that are being mapped. For all of the human gene loci, about a third are variable that is, the genes on such loci can exist in different forms or variants. For example, the locus for the gene that controls ear lobe shape may have on it the arrangement of DNA that produces attached ear lobes, or the arrangement of DNA that produces free ear lobes. Variations on the same gene locus are called alleles. While humans share identical genes, individuals differ in the specific alleles they possess. So the Human Genome Project is identifying the loci for all human genes and some of the alleles for those genes that have them." (Emphasis added)
"The Human Genome Project discovering the human blueprint: Gene mapping and DNA sequencing," www.science.org.au/nova/006/006box02.htm
- Independent JPEG Group, www.jpg.org.
- Tina Hesman, "The Meaning of Life: Computers are unscrambling genomes to reveal the secrets in DNA codes," Science News, Science Service, Washington, D. C.: April 29, 2000, Vol. 157, p. 284.
- John P. Pratt, "The Lord's Science in the New Millennium," Meridian Magazine, Feb. 18, 2000, Heading: Deciphering the Code of Life.
- "Knowing the function of introns seemed critical for sorting out these issues. There were many ingenious suggestions. Some thought introns were just another example of the apparently non-utile "junk" DNA which littered the DNA of many eukaryotes. However, some principles to guide investigation of a possible error-checking role were presented (Forsdyke 1981), and there is now growing evidence that introns play such a role (Forsdyke 1995a,b)."
Donald R. Forsdyke, "Introns and Exons," Department of Biochemistry, Queens University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada: 1995, post.queensu.ca/~forsdyke/introns.htm
- "The failure of Galileo's high gain antenna deployment has resulted in four orders of magnitude degradation in the planned Earth-received signal level. In order to conduct a meaningful mission, extraordinary changes have been made to both the spacecraft and ground communication systems. These changes include a new packetized telemetry format, new error-correcting codes, new modulation, new ground receivers, antenna arraying, and extensive use of data compression. With these modifications in place, about 70% of the originally planned Galileo mission science objectives will be achieved."
Leslie J. Deutsch, "The New Galileo Communication System," Jet Propulsion Laboratory: 1995, jpltrs.jpl.nasa.gov/1995/95-0089.pdf
The author performed an experiment with the popular PKZIP 2.5 software to generate a 32 bit CRC (cyclic redundancy check) error detection code for a 11,606 byte file containing an HTML version of the Declaration of Independence. For the original file the 32 bit CRC code was 'fcc5c069' in hexadecimal format. A one bit change to the file that changed the "July 4, 1776" date to "July 5, 1776" resulted in a new CRC code of '61d96a2a' hex, totally different from the first CRC. If the DNA code does actually include error correction sequences, it would add another amazing information processing layer to our models of living systems.
- Hesman, op. cit., p. 286.
- "DNA sequences usually dismissed as junk DNA without any function actually help determine what genes on the X chromosome become suppressed. .... [Evan Elchler's] latest work has given him a greater appreciation for the possibility that DNA sequences such as L1 elements have some role in human biology. 'We as scientists have this preconceived notion, based on very little data, that this selfish DNA is nothing more than junk. I think junk is a very unfortunate term. It's more a reflection of our ignorance.'"
John Travis, "Silence of the Xs: Does junk DNA help women muffle one X Chromosome?" Science News, Science Service, Washington, D. C.: August 5, 2000, Vol. 158, No. 6, pp. 92-94.
"Scientists began the next and far more challenging step in explaining the molecular underpinnings of life. It's called proteomics the cataloging and analysis of every protein in the human body. .... biotech firms ... have launched their own proteomics programs, some focused on protein structures, other trying to determine where in the body different proteins are produced and how each is controlled." (Emphasis added).
Unmesh Kher, "Beyond Genomics. The Next Frontier: Proteomics," Time Magazine, op.cit., p. 29.
- The genome sequencing has allowed for more research into genes that code for RNA instead of proteins. A class of RNA called "small nucleolar RNAs or snoRNAs .... [that direct] an enzyme to a certain spot in ribosomal RNA, which is a component of the cell's protein-building machinery." Hesman, op. cit., p. 285.
- "The map (of two RNA molecules and 31 proteins of one of the subunits of a bacterial ribosome) suggests where and how the ribosome chemically stitches amino acids into a protein." J. Gorman, "Ribosomes Reveal Their RNA Secrets," Science News, Washington, D. C., August 12, 2000, Vol. 158, p. 100
- Teachings of the Presidents of the Church: Joseph F. Smith, Salt Lake City: 1998, p. 88.
- Pratt, op. cit., reviewing Antonio R. Damasio, "How the Brain Creates the Mind," Scientific American, New York, December 1999.
- Joseph Fielding Smith, Gospel Doctrine: Selections from the Sermons and Writings of Joseph F. Smith, Salt Lake City, 1919, p. 61.
It is interesting to also study the use of the word "execute" in the scriptures that sometimes seems to use the computer science "program control" meaning of the word. This includes D. & C. 88:40: "For intelligence cleaveth unto intelligence; wisdom receiveth wisdom; truth embraceth truth;... judgment goeth before the face of him who sitteth upon the throne and governeth and executeth all things. (emphasis added)
- The power of the atonement of Jesus Christ in the sustaining of life is emphasized in Jacob's discourse on the atonement:
"For I know that ye have searched much, many of you, to know of things to come; wherefore I know that ye know that our flesh must waste away and die; nevertheless, in our bodies we shall see God. ....Wherefore, it must needs be an infinite atonement save it should be an infinite atonement this corruption could not put on incorruption. Wherefore, the first judgment which came upon man must needs have remained to an endless duration. And if so, this flesh must have laid down to rot and to crumble to its mother earth, to rise no more. O the wisdom of God, his mercy and grace! For behold, if the flesh should rise no more our spirits must become subject to that angel who fell from before the presence of the Eternal God, and became the devil, to rise no more." (2 Nephi 9:4, 7-8) (Emphasis Added)
See also: Tad R. Callister, The Infinite Atonement, Deseret Book, Salt Lake City, 2000, p. 70. "The Atonement was both an exercise of power and an acquisition of power. ... The exercise of those powers necessary to endure the sufferings of all mankind may in turn have opened the door to the additional powers needed to resurrect, to redeem, and to exalt. ... 'Worthy is the Lamb that was slain to receive power' (Revelation 5:12);"
- Daniel J. Fairbanks, "The Arts, the Sciences, and the Light of the Gospel," BYU Devotional, May 2, 2000, p. 4. speeches.byu.edu.
- Dr. Fairbanks: "I have my students read Mendel's classic work because it is such a superb example of scientific experimentation and objectivity. However, Mendel also left us some powerful religious writings."
Further extracts of Mendel's poem:
"But unfading are the laurels of him
Who earnestly and zealously strives
To cultivate his mind,
Who with the full light of his understanding
Seeks and finds the mysterious depths of knowledge,
Of him in whose development the germ
Of glorious discovery implants itself."
Ibid., p. 5.




